Archive
A list of Windows XP accessibility features and related keyboard shortcuts
|
Contains information about the FilterKeys accessibility feature, which enables a user with disabilities to set the keyboard repeat rate (RepeatKeys), acceptance delay (SlowKeys), and bounce rate (BounceKeys). |
|
|
Contains information about the high contrast accessibility feature. |
|
|
Contains information about the MouseKeys accessibility feature. When the MouseKeys feature is active, the user can use the numeric keypad to control the mouse pointer, and to click, double-click, drag, and drop. By pressing NUMLOCK, the user can toggle the numeric keypad between mouse control mode and normal operation. |
|
|
Contains information about the SerialKeys accessibility feature, which interprets data from a communication aid attached to a serial port as commands causing the system to simulate keyboard and mouse input. |
|
|
Contains information about the SoundSentry accessibility feature. When the SoundSentry feature is on, the computer displays a visual indication only when a sound is generated. |
|
|
Contains information about the StickyKeys accessibility feature. When the StickyKeys feature is on, the user can press a modifier key (SHIFT, CTRL, or ALT) and then another key in sequence rather than at the same time, to enter shifted (modified) characters and other key combinations. |
|
|
Contains information about the ToggleKeys accessibility feature. When the ToggleKeys feature is on, the computer emits a high-pitched tone whenever the user turns on the CAPS LOCK, NUM LOCK, or SCROLL LOCK key, and a low-pitched tone whenever the user turns off one of those keys. |
Pasted from <http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/dd317974(v=vs.85).aspx>
Watch these keys:
- Right Shift for eight seconds (Switch FilterKeys on or off)
- Left Alt+left Shift+Print Screen (Switch High Contrast on or off)
- Left Alt+left Shift+Num Lock (Switch the MouseKeys on or off)
- Shift five times (Switch the StickyKeys on or off)
- Num Lock for five seconds (Switch the ToggleKeys on or off)
- Windows Logo +U (Open Utility Manager)
Pasted from <http://support.microsoft.com/kb/301583#method4>
In addition, this article shows and explains all the settings dialogues for accessibility options in Windows XP.
How to find your computer’s name
Common commands in Speech Recognition for all languages supported
(I cut a corner and left out the language variants ZH-TW and EN-UK, sorry, we do not teach those here):
How to resolve error “Speech Recognition could not start because the language configuration is not supported”
- Problem: I have seen this error
 ,
, - Root cause: when the display language and speech language do not match (the latter is set to default to the former in the LRC, but it seems they can get out of sync), as you can witness here (English display does not match Chinese speech recognition):

- Solution: Follow the instructions in the error message, i.e.
- Access the Speech recognition control panel here:

- Then change the speech recognition language to match the display language, like I am doing here:
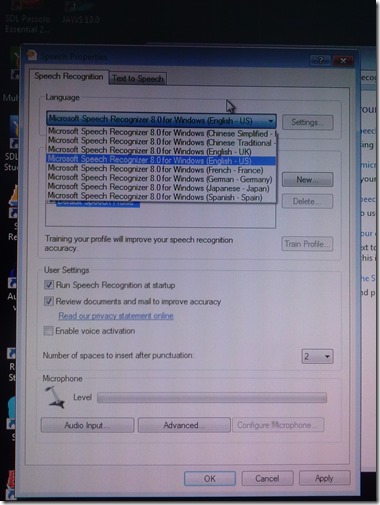
- Quick workaround: Not sure about how quick, but in the LRC, you can also just try and restart the computers, they are “frozen” to a default configuration in display and speech recognition language (English/English – matches).
Example 5: Watch how you can dictate to Windows speech-recognition (e.g. in English) and correct results in MS-Word
- Important: Listen carefully: I am not a native speaker, but have a reasonably low amount of errors, because it enunciate, speak clearly and slowly, and separate the words.
- Consider it part of the exercise that you will have to re-read and re-type some your output – use track changes in MS-Word:
- Make it a game: How good can you get?
- If you get really good at it, make a screencast like this one and include it in your Mahara ePortfolio as authentic evidence of your foreign language proficiency.
- Overall, it’s like how I refer to cycling: Beats walking. Anytime.

How to type phonetic symbols on a computer
- Web-based On-screen-keyboards (point-and-click; low learning curve, but no fast typing speed; typing into a textbox from where you can copy/paste the result into other programs):
- http://westonruter.github.com/ipa-chart/keyboard/: Sounds are systematically organized. Suitable for learners, but also good for teacher demonstrations.

- Partially based on keyboard shortcuts: http://www.ipatrainer.com/user/site/index.php?pageID=ipawriter:
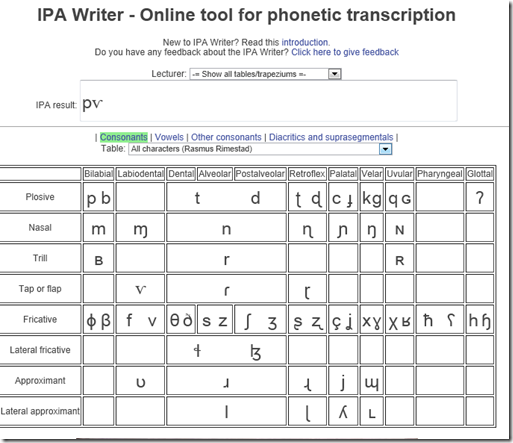
- http://ipa.typeit.org/full/: Other than the English version, the full version includes non-English sounds. The interface is optimized for fast typing (sorted by keyboard key). Presumably better for teachers using a screen projector as a whiteboard.

- i2speak.com (reviewed here earlier):


- Update: Richard Ishida’s seems also impressive,
- http://ipa.typeit.org/full/: Other than the English version, the full version includes non-English sounds. The interface is optimized for fast typing (sorted by keyboard key). Presumably better for teachers using a screen projector as a whiteboard.
- http://westonruter.github.com/ipa-chart/keyboard/: Sounds are systematically organized. Suitable for learners, but also good for teacher demonstrations.
- Windows-based:
- http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/resource/phonetics/: MS-Windows keyboard layout. May be good for even faster typing, if you can memorize the keyboard layout or add keyboard stickers (we unfortunately have too many languages vying for our hardware keyboard space already). Requires download & installation (may be added to the LRC keyboards during next imaging if we receive enough requests).

- http://staff.washington.edu/dmontero/IPACharmap/.

- http://sourceforge.net/projects/allchars/: If you are use to the ALT+### method of entering characters and are still on XP, this may be for you: You can generate your own keyboard shortcuts for phonetic characters.
- MS-Word:
- http://email.eva.mpg.de/~bibiko/downloads/uniqoder/uniqoder.html: Allows to select IPA-Symbols from a toolbar. Untested.
- http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/resource/phonetics/: MS-Windows keyboard layout. May be good for even faster typing, if you can memorize the keyboard layout or add keyboard stickers (we unfortunately have too many languages vying for our hardware keyboard space already). Requires download & installation (may be added to the LRC keyboards during next imaging if we receive enough requests).
- There are also always X-Sampa and CXS and ASCII-IPA: ways of writing IPA in plain ASCII messages – but yet another thing to teach novices in phonetics may be a bridge too far.
Example 6: How even a false beginner can work with foreign language Speech recognition on Windows 7 Enterprise
- Executive summary: Don’t let initial poor speech recognition results discourage your from using this feature. Results will much improve if you go through a few minutes of the built-in voice training for speech recognition. Like in the last 30 seconds of this video.
- With the upgrade to Windows 7 Enterprise in the LRC – and the continued availability of high-quality Sanako headphones on the majority of LRC PCs – , we can now offer speech recognition in a number of foreign languages – including French.
- This feature can be used for language learning exercises, including dictation, like in this example. How robust is windows 7 speech recognition?
- You can expose yourself to some embarrassingly bad French in this screencast – and that is the point. (My French is limited to a mere 2 high school years of 3-hour per week voluntary French studies, more than 30 years ago, no practice since).
- The screencast shows how even a (false) beginner can,
- 0:00-1:00: from terrible initial results,
- 11:45-12:10: considerably improve (not make perfect!) the foreign language (here French) speech recognition on Windows 7,
- 1:00-10:40: by going through the built-in voice training.
- The LRC computers are “frozen”between reboots, but students still need to train them only once, since they can back up and restore their training data easily.

- (This is not proof of the overall validity of the recognition – for that, you are better off watching this screencast with Windows 7 Enterprise speech recognition in German).
Blog Stats
- 512,774 hits

Questions? Read the About. Or just ask me a quick
FAQs for LRC student staff or for students or for teachers. To search our FAQs, in the browser addressbar, add after "https://plagwitz.wordpress.com/feed/?tag=faqs+/" "+TAG1" (from tag cloud below) OR "https://plagwitz.wordpress.com/feed/tag=faqs
&category_name=" "CAT1" (from category hierarchy below). OR search both categories and tags, and multiple TAGs/CATs (connect with "," for OR-search, with "+" for AND-search), like so: https://plagwitz.wordpress.com/feed/?tag=TAG1+TAG2+...TAGn&category_name=CAT1
+CAT2+...CATn"
Other ways to find help
If you cannot find it here, look there: 5,500 Language-Learning Links and Programs for learning or teaching 150 languages
Shortcuts:Our Lists, Our Maps, LRC Staff Moodle Site,LRC Project Moodle Site, 49erexpress, UNCC Moodle, Student Recordings: s:claslcslrcsanakostudent
Learning usage samples: Sanako oral exam, Kaltura webcam presentation, Dictation with speech recognition, Sanako written exam, Chinese and Japanese interactive stroke-order practice
Test the Sanako Installer, Webbrowser Popup Konfigurator for XP, or Windows7, faster LRC TeacherPC Log-in Let MS facilitate diacritics writing by installing for you US-International keyboard layout
This is my personal blog (Google+). The views expressed on these pages are mine alone and not those of my employer. The information in this weblog is provided “AS IS” with no warranties, and confers no rights.
Top Posts & Pages
- How to export BMC Remedy data into Excel other than via copy-paste
- Speaking dictionary/pronunciation help, Part 2 – The technology: Installation & configuration of the free Windows XP text-to-speech wizard
- How to fix “Print to OneNote”, “OneNote cannot find a page on which to insert your printout”
- Use parentheses to search in MS-OneNote for a string that includes punctuation
- How to fix Canon Vixia “Cannot write on card” error when starting recording by initializing
- How to display Furigana phonetic guide for Japanese Kanji in MS-Word 2010
- How to type phonetic symbols on a computer
- How to map network shares using VBScript and WMI
- Mac Mini (Mid 2010) Overview
- How to unstick the ALT key in KRDC RDP sessions
Top Clicks
Categories
- Area-is-any (194)
- Back office (10)
- Coed432 (2)
- LRCRoomCoed435a (1)
- LRCRoomCoed436 (4)
- COED037 (14)
- presenter-computer (9)
- student-computers (6)
- faculty-offices (3)
- LRCRoomCoed433 (68)
- iMacs (14)
- Listening-Stations (23)
- printer (1)
- Reception-desk (33)
- small-group-work-spaces (12)
- TV-viewing-area (3)
- LRCRoomCoed434 (117)
- Presenter-Computer (78)
- Student-Computers (69)
- MGB-36 (4)
- Back office (10)
- audience-is-any (683)
- Computer and Internet (3)
- Utilities (1)
- Genre-is-any (643)
- announcements (21)
- bad-ideas-and-other-mistakes-samples (1)
- cheat-sheets (2)
- checklists (31)
- documentation (151)
- feedback (2)
- flowcharts (3)
- Internal (1)
- learning-materials (86)
- learning-usage-samples (21)
- marketing (18)
- Notes (228)
- Glitches&Errors (190)
- Learning-logs (24)
- mental-notes (20)
- policies (5)
- Practice&Demos (26)
- conferences (17)
- tradeshows (3)
- projects (9)
- proposals (13)
- reports (11)
- research (2)
- reviews (3)
- step-by-step-guides (38)
- table-of-contents (8)
- training (80)
- clinics (6)
- faculty-showcases (2)
- workshops (29)
- Institution-is-any (193)
- Institution-is-Aston-University (13)
- Institution-is-Drake-University (2)
- Institution-is-London-Metropolitan-University (33)
- Institution-is-Loyola-University-Maryland (27)
- Institution-is-Queen's-University (1)
- Institution-is-University-of-Michigan-Dearborn (3)
- Institution-is-University-of-North-Carolina-Charlotte (120)
- Institution-is-University-of-Tampa (4)
- K12 (1)
- Learning-activity-is-any (82)
- assessments (44)
- assignments (35)
- classroom-activities (8)
- grading (11)
- presentations (4)
- Learning-Tool-is-any (683)
- Classroom-technology (162)
- erepository (19)
- hardware (86)
- audiovisual (28)
- faculty-equipment (10)
- film-studies-equipment (14)
- furniture (1)
- headphones (18)
- mobile-computing (8)
- mobile-phones (4)
- tablets (4)
- phones (6)
- audiovisual (28)
- Media (32)
- multimedia-recording (79)
- software (215)
- Authoring-tools (3)
- Polls (2)
- GIS (4)
- office-software (87)
- Operating-system (20)
- os (16)
- recording-software (15)
- translation-software (9)
- web-browsers (12)
- Authoring-tools (3)
- software-old (7)
- textbooks (22)
- websites (208)
- blog (12)
- eportfolio (7)
- lab-portal (4)
- lms (95)
- Metrics (22)
- Analytics (7)
- Visualizations (8)
- Multimedia-is-any (269)
- animated-GIFs (43)
- Audiofiles (1)
- Charts (8)
- compiledcode (17)
- Documents (15)
- forms (4)
- Interactive-documents (1)
- Photos (11)
- Pictures (1)
- polls (1)
- Scans (2)
- Screencasts (87)
- screenshot-albums (5)
- Screenshots (16)
- Slideshows (24)
- sourcecode (21)
- Spreadsheets (35)
- Videos (13)
- Personal (22)
- second-language-acquisition (249)
- 4-skills (216)
- Grammars (4)
- Proficiency-Levels (36)
- Absolute-Beginner (19)
- Advanced (28)
- Beginner (26)
- Intermediate (29)
- Near-Native (9)
- Syntax (2)
- Vocabulary (52)
- Corpus-linguistics (16)
- corpora (9)
- Dictionaries (18)
- Corpus-linguistics (16)
- service-is-any (454)
- service-is-applying-learning-tools (23)
- service-is-assessing (21)
- service-is-configuring-learning-tools (34)
- service-is-documenting (70)
- service-is-evaluating-learning-tools (38)
- service-is-hr-managing (15)
- service-is-it-managing (20)
- service-is-learning-materials-creation (90)
- service-is-library (99)
- service-is-outreach (2)
- service-is-programming (66)
- service-is-project-managing (16)
- service-is-testing (2)
- service-is-testing-troubleshooting-debugging (71)
- service-is-training (14)
- service-is-tutoring (19)
- Study-program-is-any (314)
- all-languages (228)
- Film-studies (38)
- Interpreting (36)
- Translation (27)
- Teaching-delivery-format-is-any (27)
- technology-domains-is-any (853)
- digital-humanities (7)
- e-commerce (2)
- e-infrastructure (471)
- e-languages (297)
- e-learning (103)
- e-research (2)
- Uncategorized (38)
- unit-is-any (4)
Archives
- September 2017
- April 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- March 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- June 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- June 2009
- May 2009
- April 2009
- March 2009
- February 2009
- September 2008
- August 2008
- July 2008
- June 2008
- March 2008
- January 2008
- November 2007
- August 2007
- July 2007
- June 2007
- December 2006
- June 2006
- May 2006
- April 2006
- March 2006
- February 2003






