Archive
Archive for the ‘office-software’ Category
Announcing new MS-Word templates for writing assignments during face-to-face-classes in the LRC
2012/11/08
Leave a comment
- Benefits
- MS-Word is technology that has become “transparent”for most users:
- Have teachers focus on assignment pedagogy, not authoring technology.
- Have students focus on the target language, not authoring technology.
- Document is protected (for restricting formatting to predefined Word-styles):
- Have students focus on form or content, but not on distracting formatting issues.
- Styles are designed to facilitate teacher monitoring students’ work using Sanako screensharing, like so:
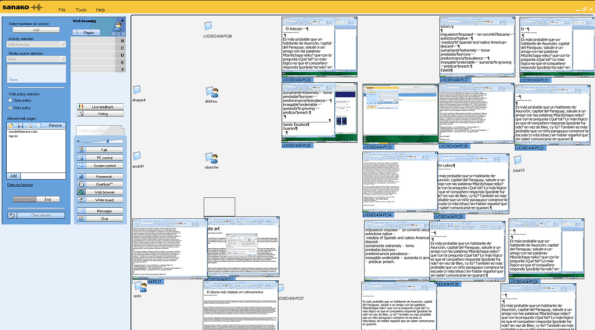
- Take advantage of MS-Office Proofing tools (templates are preset for your target language).
- Take advantage of easy assignment file management with Sanako homework activity.
- Take advantage of internet lookup process, especially pedagogical if you combine with Sanako controlled-web-browsing activity
- MS-Word is technology that has become “transparent”for most users:
- Requirements:
- Teacher
- The easiest is to save the writing template for your language in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Templates\1033 (or if your run 32-bit MS-Word on a 64-bit Windows, C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Templates\1033)
- Then base your writing assignment document on the template (e.g. by double-clicking the template in the folder you saved it to).
- Then save your writing assignment to your class material folder on the Sanako network share (from the office or in the LRC).
- In class, launch the Sanako homework activity.
- Student: none other than downloading and submitting the Sanako homework.

- Teacher
Categories: announcements, audience-is-teachers, classroom-management-system, e-languages, office-software, Presenter-Computer, service-is-configuring-learning-tools, service-is-learning-materials-creation, service-is-programming, Student-Computers, Writing
homework-activity, MS-Word, sanako-study-1200, screensharing, templates, trpStudentWriting, web-browsing-activity
How teachers can use MS-Word Mail merge with filtering and if-then-else to quickly provide personalized feedback based to students depending on grade
2012/10/18
Leave a comment
- Intelligence is adaptation to feedback. Providing personalized feedback to students depending on their performance could make student development much more successful.
- Intelligence is expensive. How can the teacher provide personalized feedback time-efficiently? Likely by blending artificial intelligence with her own.
- Sounds like Sci-fi? A great practical example, using existing familiar IT infrastructure, you can find here: MS-Word’s (2010; 2007 works the same) mail merge feature, on the basis of a downloaded Moodle gradebook with student results, can customize semi-automatically your reusable feedback email message template to individual recipient’s performance and needs:
- Step-by-step instructions: http://teaching.uncc.edu/moodle/grade-book/how-to/using-mail-merge-grade-book.
- Screencast of the webinar instruction: http://mt202.sabameeting.com/SiteRoots/main/User/GuestAttend.jhtml?pb=true&s_guid=0000018151460000013a0a22cfb39443&domain=/Customers/uncc&domain=/
Categories: audience-is-teachers, e-learning, grading, lms, office-software, Screencasts, step-by-step-guides
MS-Word
Why MS-OneNote may let you run out of storage space here
2012/10/04
Leave a comment
I am running into out of file space issues in a number of applications. Turns out that OneNote is the culprit, but it is not obvious from the OneNote Save & Backup why: 
The Reason is that Application Data\Microsoft\OneNote gets redirected to the personal network drive:\My documents folder, the disk quota for which is limited:
Protected: How to show the Developer Tab in the MS-Word 2007/2010 Ribbon
2012/10/04
Enter your password to view comments.
Categories: audience-is-teachers, documentation, office-software, Writing
2007, 2010, developer-tab, MS-Word
How best to edit PDF here
2012/08/18
Leave a comment
The college provides each faculty and staff member with a full version of Adobe Acrobat (with editing capabilities) on their office computer. If it is not already installed, you can submit a request here.
Foreign language support in LRC MS-Office 2010
2012/08/17
Leave a comment
- A full set of proofing tools is available, thanks to MS-Office Language Packs installed on the Windows 7 computers, for all non-classical languages studied here:
-
Language Native name Arabic العربية Chinese (Simplified) 中文(简体) Chinese (Traditional) 中文 (繁體) English English French français German Deutsch Greek Ελληνικά Hebrew עברית Hindi हिंदी Italian italiano Japanese 日本語 Korean 한국어 Polish polski Portuguese (Brazil) Português Portuguese (Portugal) português Russian Русский Spanish español - Some languages have only limited features provided by the MS-Language Interface Pack:
-
KiSwahili Kiswahili Persian (Farsi) فارسی Yoruba ede Yorùbá
Categories: Arabic, audience-is-students, audience-is-teachers, English, Farsi, French, German, Greek (modern), Hindi, Italian, Japanese, Korean, office-software, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, Swahili, Writing, Yoruba
2010, language-interface-packs, language-packs, ms-office










